Stay updated on news, articles and information for the rail industry
SPONSORED
AGICO Group - Branded Feature
Comparison Of Ballasted Track And Non-Ballasted Track
Visit railway-fasteners.com for more information >>
As the foundation of whole railway track system, railroad track provides a plat for train. In general, railroad track is consists of rail, rail joint, railroad tie and railroad fasteners, etc. Railroad track is also known as track or railway track. As we all know, ballasted track and non-ballasted track are two typical kind of railway track. There are plenty of differences between ballasted track and non-ballasted track, such as composition, construction, maintenance, cost, and so on. As a proportional railway components manufacturer in china, agico Rail contrast ballast track and non-ballasted track.
Ballasted track
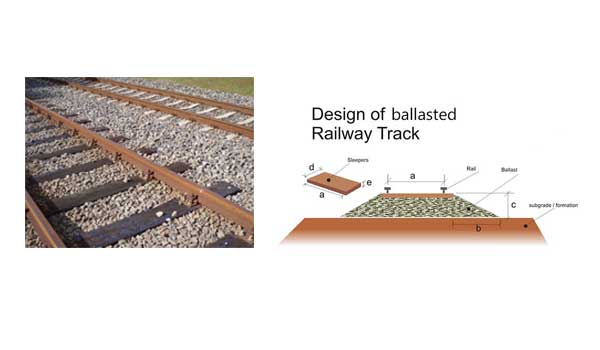
Ballasted track is a type of traditional railway tracks. Ballasted track is commonly composed of steel rail, railroad tie, railway fasteners and ballast bed. Theoretically, ballasted track is the creation of railway track development. In 1865, the basic structure of the modern track structure was completed. Generally, laying ballast under the railway sleepers to reduce the stress on the ground. A layer of gravel was laid between ground and railway sleeper to form the track bed. Track bed (ballast bed) can improve the flexibility and drainage performance of railway track. Ballasted track also make track easy to repair. The traditional track whose bed is made up of ballast, also called ordinary track and what is often known as ballasted track.
Advantages
- Ballasted track requires low investment cost.
- Ballasted track is usually easy to lay.
- Ballasted track has good drainage performance.
Disadvantages
- Train run on the ballasted track with banged sound and low speed. so that, passengers may feel uncomfortable.
- Ballasted track is easy to be deformed.
- Ballasted bed requires frequent and costly maintenance.
- Train speed is limited on the ballasted track.
- Ballasted track has poor life expectation (about 15-20yrs).
- Ballasted track produce more pollution by releasing dust from ballast.
- Ballasted track has higher noise level than non-ballasted track. It is necessary to take effective noise reduction measures.
Non-ballasted track

Non-ballasted track, also called ballastless track, is the railway track whose bed is composed of concrete and bituminous mixture, etc. Generally, non-ballasted track is made up of steel rail, railway fasteners and slab. Non-ballasted track’s railway sleeper is formed by concrete casting. Instead of ballast bed, steel rail and railway sleeper is laid on the concrete track. There is no doubt that non-ballasted track is the advanced track technology in the world. Slab track is one of the most important types of non-ballast track structure.
Advantages
- Non-ballasted track need less maintenance, save cost.
- Non-ballasted track can reduce dust and beautify the environment.
- Non-ballasted track has great ride performance and stability.
- Non-ballasted track has long durability and service life (about 50-60yrs).
- Non-ballasted track has high train speed and make passengers feel comfortable.
Disadvantages
- Non-ballasted need more investment cost than ballasted track.
- Non-ballasted track cannot be laid in some area like clay deep cutting, soft dirt road and earthquake area.
- The most serious drawback of non-ballasted track is that possibilities for improvement are limited.
Application

As two common types of railroad track, ballasted track and non-ballasted track both have their merits. When it comes to application, ballasted track is used in the normal speed railway and fast speed railway. Non-ballasted track high speed railway normally adopt non-ballasted track. There are some exceptions, for example, in China and France, ballasted track is individually applied in the high speed railway.
Visit railway-fasteners.com for more information >>


 2025 MOW Spending Report: Passenger-rail programs
2025 MOW Spending Report: Passenger-rail programs
 Gardner steps down as Amtrak CEO
Gardner steps down as Amtrak CEO
 Guest comment: Oliver Wyman’s David Hunt
Guest comment: Oliver Wyman’s David Hunt
 Women of Influence in Rail eBook
Women of Influence in Rail eBook
 railPrime
railPrime



